1. Overview
DDS3666 single-phase electronic watt-hour meter (hereafter: watthour meter)adopts
advanced ultra-low power consumption solid-state integrated circuit technology and
SMT advanced technology for measuring AC single-phase active energy.
The performance indicators of this product comply with IEC 62053-21:2003 and
GB/T17215.321-2008 "1 and 2 static AC active power meters" for single-phase static electricity meters.
The communication protocol is in accordance with the DL/T 645 -- 1997 and DL/T 645 -- 2007
Multifunctional electricity meter Communication Protocol or MODBUS communication protocol.
2. Functions and characteristics
2.1 It has the characteristics of wide load, high accuracy, high reliability,
high sensitivity, flat error curve and low power consumption.
2.2 With bidirectional metering function, can accurately measure positive and reverse bidirectional active energy,
according to the total power metering, liquid crystal display, data permanent storage.
2.3 The passive pulse output interface with optical coupling isolation is adopted.
2.4 With infrared communication interface, baud rate of 1200 fixed.
2.5 RS485 communication port. The baud rate is 1200(DL/T645) and 4800(MODBUS) by default.
The baud rate can be 1200, 2400, 480, 9600. (Optional)
2.6 Instrument using LCD liquid crystal display, generous intuitive.
Total electric quantity data is displayed on the upper row of the instrument, constant constant of the lower row wheel,
table number, voltage, current, power, power factor, frequency data, each data wheel display time is 5 seconds.
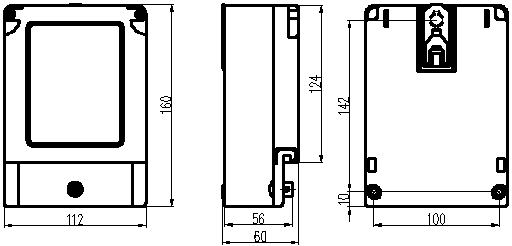
3. Drawing of watthour meter as following:
4. FAQ:
1.Q:What is an optical coupled isolator?
A:An opto-isolator (also called an optocoupler, photocoupler, or optical isolator) is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals
between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the signal.
2.Q:What is the function of optical isolation?
A:An optical isolator is a device that only allows unidirectional transmission of the optical signal. It is often used in optical systems to
avoid unwanted optical reflections. For example, a single-frequency semiconductor laser is very sensitive to external optical feedback.